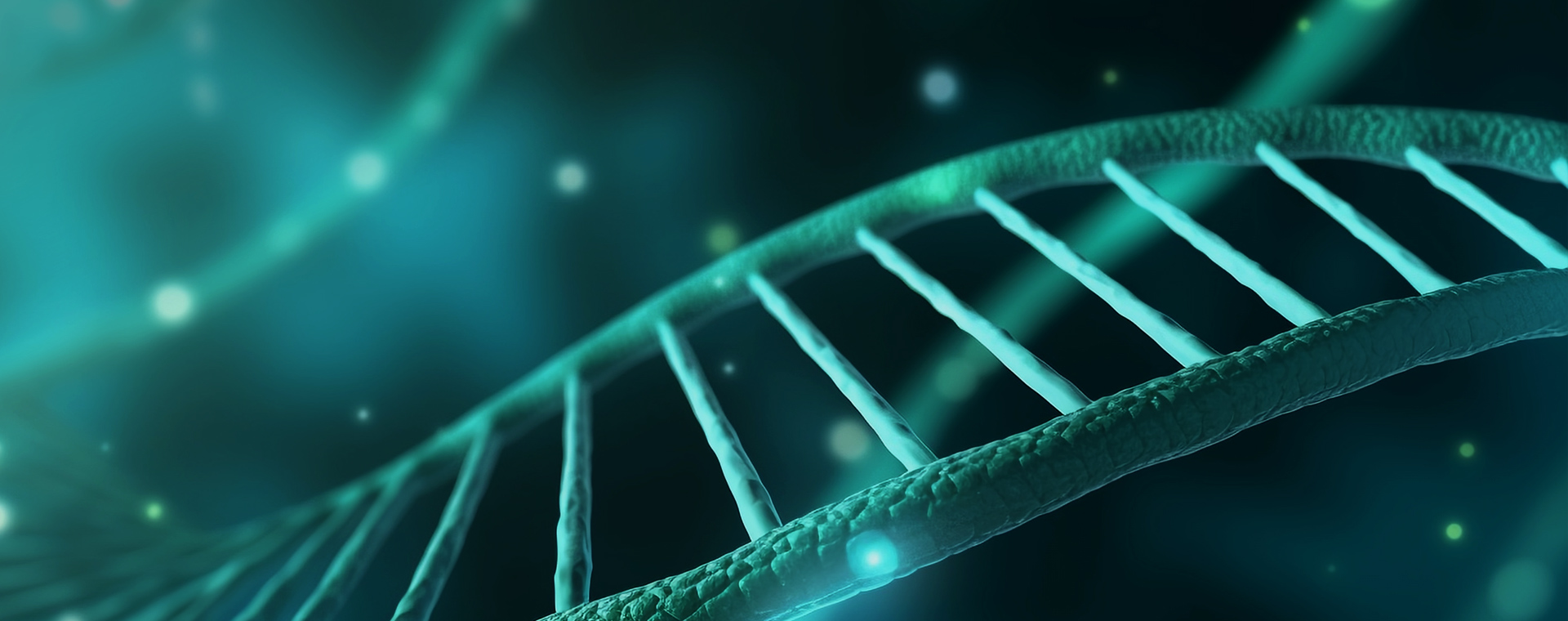



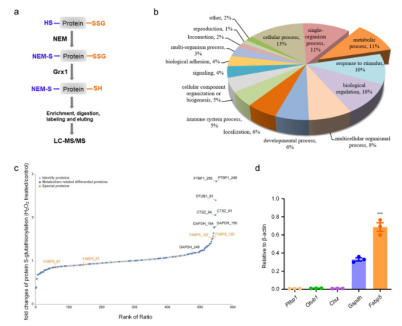
氧化条件下巨噬细胞中蛋白质S-谷胱甘肽修饰的改变 (Guo et al., 2021)
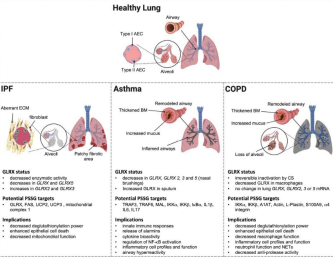
蛋白S-谷胱甘肽化状态变化影响肺部疾病(Chia et al., 2020)


1.Decreased Expression of the Host Long-Noncoding RNA-GM Facilitates Viral Escape by Inhibiting the Kinase activity TBK1 via S-glutathionylation (IF= 43.474, Q1, Immunity)
S-谷胱甘肽化调节TBK1 活性并影响先天免疫和病毒逃逸
2.Oxidative stress-induced FABP5 S-glutathionylation protects against acute lung injury by suppressing inflammation in macrophages (IF=16.6,Q1,Nature communication)
氧化应激诱导的 FABP5 S-谷胱甘肽化通过抑制巨噬细胞炎症来预防急性肺损伤
3.S-glutathionylation of Hsp90 enhances its degradation and correlates with favorable prognosis of breast cancer (IF=10.787,Q1,Redox Biol)
Hsp90表达及谷胱甘肽化状态可作为癌症的预后生物标志物或治疗靶点
4.Protein S-glutathionylation stimulate adipogenesis by stabilizing C/EBPβ in 3T3L1 cells (IF=5.834, Q1, FASEB J)(备注可删除)
蛋白质S-谷胱甘肽化通过稳定3T3L1细胞中的 C/EBPβ刺激脂肪生成